Transcatheter
Arterial Chemoembolization Does Not Improve Survival in Liver
Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SUMMARY:
As a treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), (TACE)
-- in which patients undergo both infusion of chemotherapy
drugs directly into the hepatic artery supplying the
liver and embolization, or blockage of small blood vessels
-- may be no more effective that chemotherapy infusion
alone, according to a study described in the December
2009 Journal of Hepatology. |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
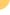 |
 |
By
Liz Highleyman
Over
years or decades, chronic hepatitis
B or C can lead to advanced
liver disease, including liver
cancer. HCC is a difficult form of cancer to treat, in part
because it is often diagnosed late.
Infusion
of chemotherapy drugs directly into the liver's blood supply has
been shown to be effective for HCC, given that liver tumors tend
to be highly vascular. The embolization procedure blocks small
blood vessels so they cannot carry blood away from the liver --
and tumors therefore receive longer exposure to the drugs -- and
so that tumors are deprived of some of their blood supply. However,
it is not clear whether TACE lads to better outcomes than transarterial
chemotherapy infusion alone.
 |
| A
technique called transcatheter chemoembolization
is used for some patients with liver cancer or other
types of cancer that have spread to the liver. The procedure
is a way of delivering cancer treatment directly to
a tumor through minimally-invasive means. |
|
Takuji
Okusaka and colleagues from Japan conducted a multicenter, open-label
Phase 3 trial to evaluate the impact of adding embolization on
the survival of patients treated with transarterial chemotherapy.
Patients with newly diagnosed unresectable (not removable by surgery)
HCC were randomly assigned to undergo treatment using either transarterial
infusion alone or TACE.
All participants had the chemotherapy drug zinostatin stimalamer
injected into the hepatic artery. Those in the TACE group also
had gelatin sponge particles infused to block small vessels. Treatment
was repeated if follow-up computed tomography scans showed new
liver tumors or re-growth of previously treated tumors.
Results
 |
82
patients were assigned to the transarterial infusion alone
group and 79 were assigned to the TACE group; baseline characteristics
were comparable in the 2 groups. |
 |
At
the time of the analysis, 58 patients in the transarterial
infusion group and 51 in the TACE group had died. |
 |
The
median overall survival time was 679 days in the transarterial
infusion group compared with 646 days in the TACE group. |
Based on these findings, the investigators concluded, "The
results of this study suggest that treatment intensification by
adding embolization did not increase survival over [transarterial
infusion] with zinostatin stimalamer alone in patients with HCC."
Embolization can have adverse effects, including interfering with
future attempts at transarterial infusion; these findings suggest
that the long-term advantages of TACE do not justify its drawbacks.
National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, Japan; Osaka Medical
Center for Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases, Osaka, Japan; Central
Hospital and Cancer Center of Ibaraki, Ibaraki, Japan; Gastroenterological
Center, Yokohama City University Medical Center, Kanagawa, Japan;
Kinki University, Osaka, Japan; Chiba University, Chiba, Japan;
Osaka Red Cross Hospital, Osaka, Japan; Kurume University, Fukuoka,
Japan; Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan; Ogaki Municipal Hospital,
Gifu, Japan; Kyoto University School of Public Health, Kyoto,
Japan; Cancer Information Services and Surveillance Division,
Center for Cancer Control and Information Services, National Cancer
Center, Tokyo, Japan; Institute of Clinical Medicine, University
of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan.
1/29/10
References
T
Okusaka, H Kasugai, Y Shioyama, and others. Transarterial chemotherapy
alone versus transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular
carcinoma: A randomized phase III trial. Journal of Hepatology
51(6): 1030-1036 (Abstract).
December 2009.
A Forner and JC Trinchet. Transarterial therapies in HCC: does
embolization increase survival? Journal of Hepatology 51(6):
981-983. December 2009.
